| Research |
| Metamaterials |
|
| Ⅰ. III-V semiconductor-based waveguide optical device with metamaterials |
| Ⅱ.Carrier Concentration Dependent Resonance Frequency Shift in Metamaterial Loaded Semiconductor |
| Ⅲ.Semiconductor DFB Laser with Plasmonic Metal Layers for Subwavelength Confinement of Light |
|
|
| Ⅰ. Ⅲ-V semiconductor-based waveguide optical device with metamaterials |
It is a challenging task to introduce the concept of metamaterials to conventional semiconductor-based photonic devices. We hope to apply metamaterials to realize novel optical functionalities that can potentially establish a new field, meta-photonics. Some novel optical functionalities have been realized previously; for example, it has been shown that in theory, it is possible to achieve sophisticated manipulation of light such as slowing, trapping, and storing of light signals in optical waveguides. In our lab., to examine the possibility for controlling permeability and obtaining non-unity values in photonic devices, we demonstrate semiconductor-based waveguide optical devices combined with metamaterial. Figure 1 is a schematic illustration of a proposed photonic device with metamterial, which consists of a GaInAsP/InP optical multimode-interferometer (MMI) and a gold-based split-ring-resonator (SRR) array attached on the coupler. The SRR, which acts as an artificial magnetic atom, is a powerful tool for obtaining non-unity permeability. If input TE-mode light has a frequency equal to SRR resonance frequency, the SRR produces a circular current in response to an incident magnetic flux, thereby producing its own flux to enhance or oppose the incident field. Consequently, an array of extremely small SRRs operates as a metamaterial layer with non-unity permeability. We selected the form of a MMI for making each SRR not be saturated by dispersing an incident light power in the MMI. Under this condition, propagating light receives phase shift and absorption loss in the device, and then transmission intensity change occurs. |
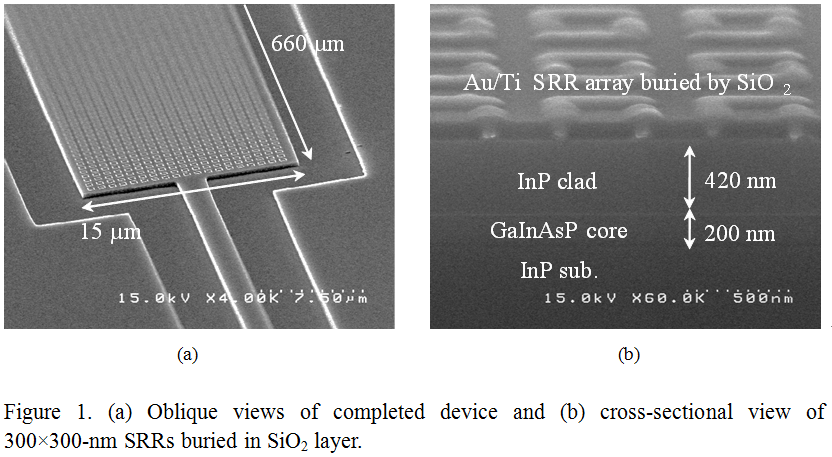 |
|
| Ⅱ.Carrier Concentration Dependent Resonance Frequency Shift in Metamaterial Loaded Semiconductor |
When applying the concept of the metamaterials to actual applications, it is indispensable to control properties of the metamaterials for tuning electromagnetic responses (i.e., tunable metamaterials). A typical way to create the tunable metamaterials is to integrate a reconfigurable material into a metamaterial structure; thereby the active tuning is achieved by applying an external stimulus. GaAs-based modulators with SRRs and metamaterial memories on a VO2 film are such device prototypes operating at a frequency of 1-10 THz. Tunable metamaterials for higher frequencies (e.g., optical frequency) is also a promising challenge for future photonic devices. They must, by necessity, have the form of a compound semiconductor device which is compatible with other conventional photonic devices. Recent researches for tunable metamaterials at optical frequencies, however, cannot meet this requirement because they normally use glass substrates, which are incompatible with other semiconductor- based photonic devices. In our lab., the effects of semiconductor carriers were explored to address the fundamental aspects of resonance tuning at around 60 THz (5-μm wavelength), bringing optical frequencies into reach for controlling the permeability in photonic devices. We examined the response of near-infrared metamaterials consisting of SRRs fabricated on semiconductor GaInAs layers with different doping levels and investigated the possibility of resonant-frequency-shift controlled by changing carriers in semiconductors. |
|
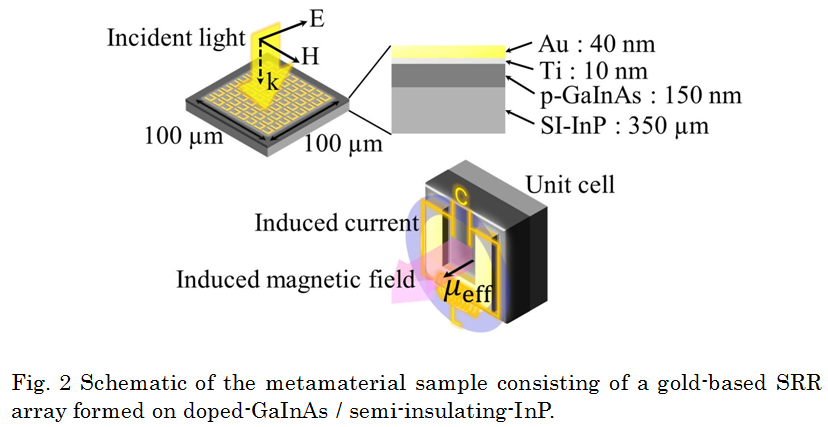 |
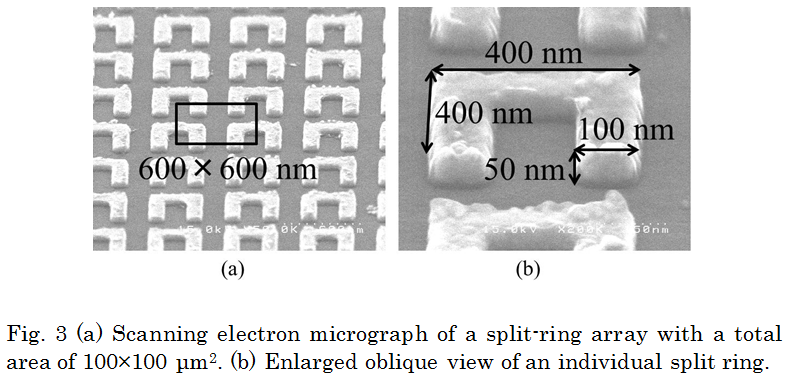 |
|
| Ⅲ.Semiconductor DFB Laser with Plasmonic Metal Layers for Subwavelength Confinement of Light |
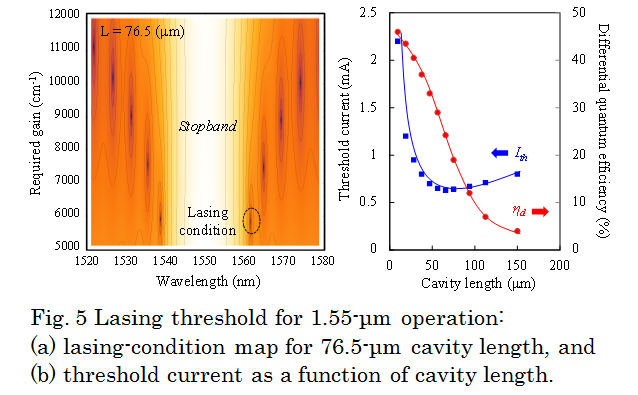
Semiconductor lasers with nanometer-sized optical cavities are indispensable components for advanced optical applications, such as on-chip optical interconnects and dense photonic integration, that need ultrasmall coherent light sources. A promising way of building such nanocavity lasers is to make use of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) to confine light in a small volume beyond the diffraction limit. A number of groups have made lasers with this idea; the examples are a microdisk laser with one-side metal coating and a CdS nanorod-on-silver laser. These devices are one step closer to the development of nanocavity lasers but incompatible with monolithic integration with other waveguide-based optical devices. To make an edge-emitting nanocavity laser integratable with other optical devices, Hill and others proposed a metal-insulator-metal structure with periodic plasmonic gaps. Their device, however, requires tight fabrication tolerances for the confinement of light and therefore is still in the experimental stage. To develop a more feasible device, we here present a novel structure, a semiconductor distributed-feedback (DFB) laser with strong confinement induced by SPPs, designed for use at 1.55-μm wavelength. |
|
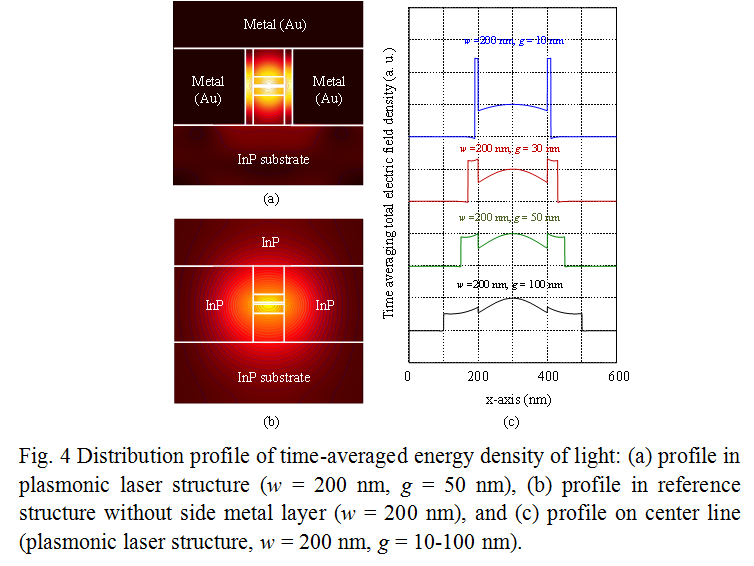 |
 |
|
|
| List of reports |
| Journal Papers |
(1) T. Amemiya, T. Shindo, D. Takahashi, N. Nishiyama, and S. Arai, “Magnetic Interaction at Optical Frequencies in InP-based Waveguide Device with Metamaterial,” IEEE J. Quantum. Electron., Vol. 47, No. 5, pp. 736-744, May 2011. |
| International Conferences |
| (1) T. Amemiya, T. Shindo, D. Takahashi, N. Nishiyama, and S. Arai, “Magnetic Interaction at Optical Frequencies in InP-based Waveguide Device Combined with Metamaterial”, Conference on Lasers and Electro Optics/International Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/IQEC) 2010, San Jose, CA, USA, CFB1 , May 2010. |
| Meeting Report |
| (1) T. Amemiya, T. Shindo, D. Takahashi, N. Nishiyama, and S. Arai, “Magnetic Interaction at Optical Frequencies in InP-based Waveguide Device with Metamaterial,” Technical Report of IEICE, LQE2009-169, pp. 123-128, Kyoto (Japan), Jan. 2010. |
| Domestic Conferences |
| (1) 雨宮 智宏、進藤 隆彦、高橋 大佑、西山 伸彦、荒井 滋久:「メタマテリアルを有するInP導波路型デバイスにおける光周波数領域での磁気応答」 The 57th Spring Meeting, The Japan Society of Applied Physics and Related Societies, 18p-P6-18, Kanagawa, Mar. 2010. |
| Books |
(1) T. Amemiya, T. Shindo, S. Myoga, E. Murai, N. Nishiyama, S. Arai. “Non-unity permeability in InP-based photonic device combined with metamaterial,” Metamaterial (ISBN: 978-953-51-0591-6), IN-TECH, pp. 215-238, Mar. 2012. |
